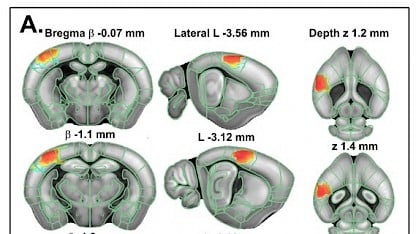
In a paper published in the Journal of Visualized Experiments, we present a simple, reliable and robust protocol for whole-brain fUS imaging in anesthetized and awake mice using our Iconeus One system.
In this study, we describe detailed procedures for using our Iconeus One functional ultrasound system to acquire 3D fUS data in anesthetized and awake mice. These procedures allow researchers to carry out non-invasive volumetric and transcranial functional mapping of the mouse brain, without contrast agent and within a short time-frame.
We illustrate this feature by mapping somatosensory cortex activation following whisker stimulation, as well as acquiring resting-state 3D functional connectivity patterns for network identification. In addition to animal preparation and data collection, we also describe the procedure for visualization, atlas registration and analysis of real-time fUS signals.
Reference:
A. Bertolo, M. Nouhoum, S. Cazzanelli, J. Ferrier, J.-C. Mariani, A. Kliewer, B. Belliard, B.-F. Osmanski, T. Deffieux, S. Pezet, Z. Lenkei and M. Tanter, Whole-brain 3D Activation and functional connectivity mapping in mice using transcranial functional ultrasound imaging, Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2021, 168: e62267.